Insight ON
Digital Twin:
a Twin in Virtual Reality with Limitless Possibilities
Digital Twin is a technology to recreate a situation or a space in virtual reality that is identical to what may happen in reality and allow users to perform simulations based on various scenarios so as to help them make optimal decisions. The technology is becoming increasingly popular in different industries as users can save time and cost by making fast and accurate decisions and predict problems that may arise. How is it used in reality, and what is the future of Digital Twin like? Let’s find out.
Text by Editorial Team
Source by K-water
Digital Twin Helps Cope with Climate Crisis
Earth is suffering from accelerating global warming and growing ecological threats. According to a UN report, natural disasters have more than doubled in number around the world over the past 20 years. Natural disasters are difficult to predict and they occur in various forms, often causing astronomical damages. As natural disasters occur more frequently amid the worsening climate change, people are becoming increasingly interested in developing new technologies to predict problems and cope with them in a timelier manner.
Hailed as one of the new key technologies to help overcome climate crisis, digital twin creates a digital copy of a process in virtual reality and helps make optimal decisions through simulations, learning machine, and reasoning. In other words, a twin of a real process is created in virtual reality wherein different scenarios that may occur can be simulated. It is highly useful as users can perform tests and experiments that are impossible or difficult to do due to time and space restrictions, cost, or safety reasons.
How can this technology be used in responding to climate crisis? The European Commission is developing a digital twin of Earth under the project “Destination Earth (DestinE)” as part of its efforts to cope with the climate crisis. The goal is to complete simulations that can encompass both short-term weather events and long-term climate change by 2030. Once the simulations are completed, we will be able to visualize how the patterns of animals’ responses to rising temperature will change and how resources will be affected by the rising sea temperature. By 2030, different digital twins created under the project will be converged into a full digital twin, and various digital policies will be adopted in connection with the digital twin of Earth.
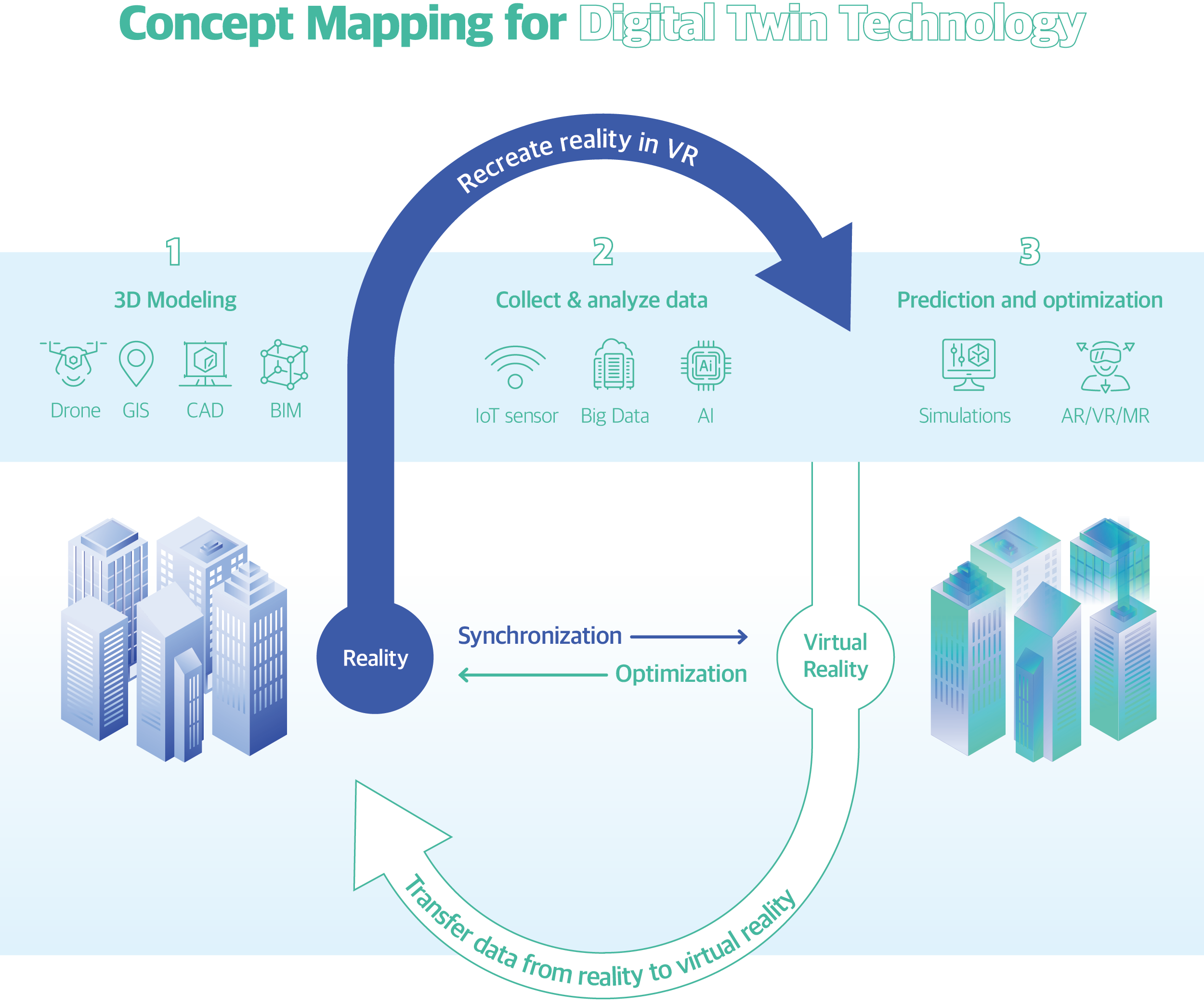
Past and Present of Digital Twin
Digital twin is not an entirely new technology. A similar technology was already used when NASA launched the spacecraft Apollo 13 in the 1960s. Simulations of the spacecraft were done in order for the ground engineers and astronauts to exchange data and prevent problems from happening.
At this point, you may be wondering: how are simulations different from digital twins? A simulation is conducted based on a set of accumulated data obtained from research on a particular process, whereas a digital twin uses big data, AI, and cloud computing to keep data updated in real time. Digital twin is different from simulation since the former involves two-way data sharing and monitoring. This way, digital twin allows users to respond to constantly changing situations in real time and control them more precisely and effectively.
Digital twin is widely used in different industries including manufacturing, energy, construction, and water management. The efficient and intelligent services made possible by digital twin are particularly evident in the public sector that is responsible for the safety and convenience of citizens. In 2018, Korea Land and Geospatial Information Corporation (LX) and Jeonju City created a standard digital twin model and implemented an administrative service model for solving urban and social issues. Daejeon City rolled out “the fire safety service” wherein outdoor and indoor spaces across downtown Daejeon are recreated in a 3D space using digital twin.
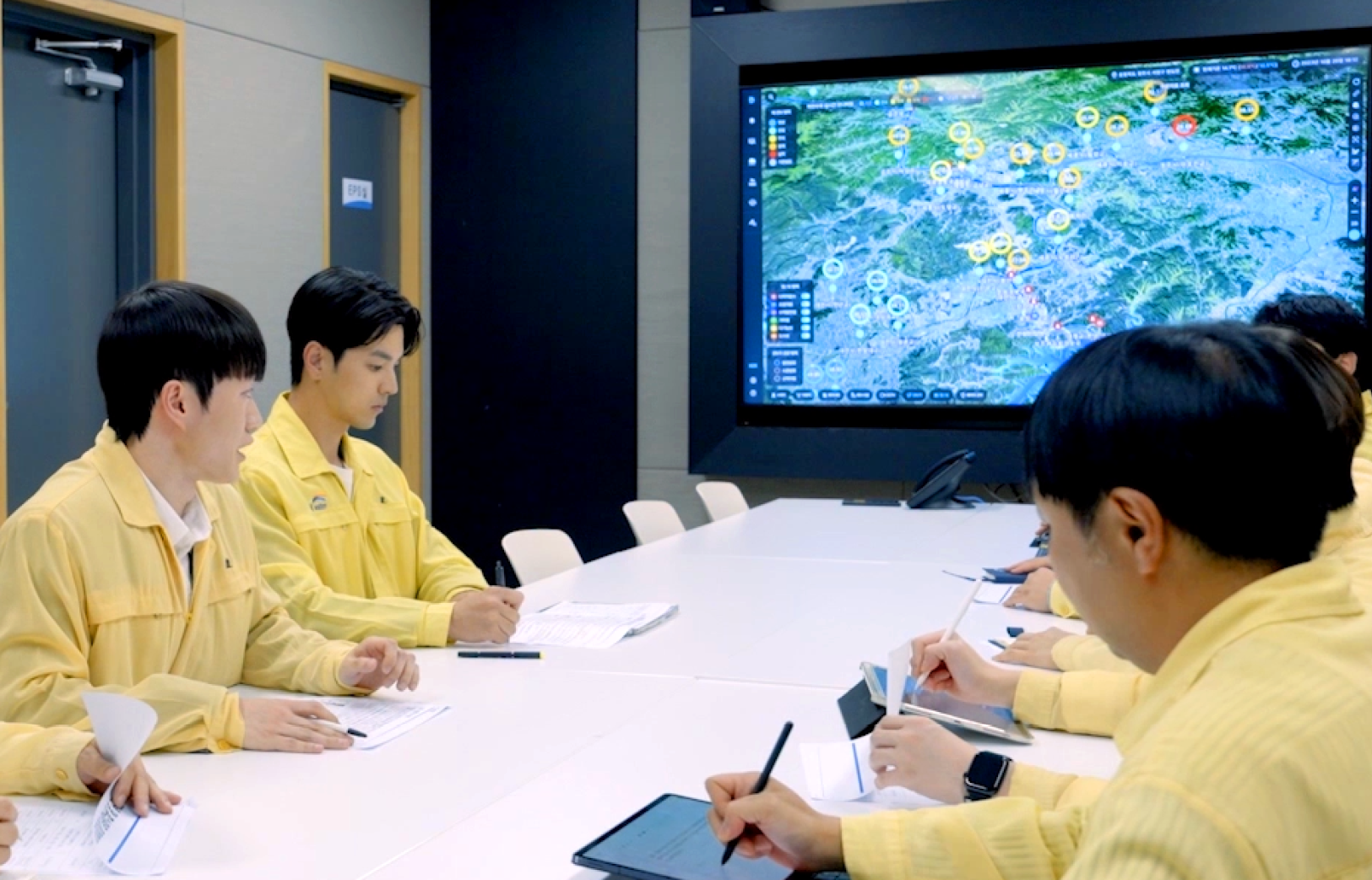

The service presents the shortest time to reach the site of fire or accident by analyzing the digital twin data including the golden time rule on extinguishing fire and saving lives and road systems. Recently, the scope of digital twin technology has been expanded to medicine, and the concept of a human body digital twin has been introduced. A digital twin of a human body allows doctors to see and access organs and parts of the body that are not visible from outside of the body and perform treatment processes and clinical simulations to develop new drugs and medical processes.

A Shift in K-water’s Water Management Paradigm
In order to deal with growing uncertainty in water management caused by climate crisis, K-water declared a shift to innovative digital water management. To this end, it is operating the digital twin-based Digital GARAM+, a smart dam safety management system, and AI water purification plants.
Introduced in 2021, Digital GARAM+ is the world’s first digital twin-based water management platform. Physical targets such as geography, rivers, and dams are copied in virtual reality, and variables including weather conditions, water gates, and water quality are chosen as input for analysis. The results are used to predict the ripple effects including changes in water levels in dams and rivers and possible damages and to make decisions on how to operate dams when heavy rains are forecast during the flood season. Currently, it is being used at dams across the country including the basins of the five major rivers: Seomjinggang, Hangang, Geumgang, Yeongsangang, and Nakdonggang.
K-water’s Digital GARAM+ is recognized globally for its excellence. Together, K-water and Naver Corp. have been selected to participate in a major digital platform project in Saudi Arabia. K-water will be involved in creating a digital twin system for flood control in Jeddah, the second largest city in Saudi Arabia, as part of the project to build a flood response platform in 5 major cities in the country.
In addition, K-water is working on the construction of a digital twin-based dam safety management system that collects big data through real-time intelligent dam observation and analyzes the data with AI. Images and videos of dam facilities produced by unmanned devices are saved, managed, and analyzed to monitor dams and affiliated facilities in a more systematic manner. With the introduction of digital twin technology, simulations on earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters can be performed to assess the safety and stability of dam facilities and help make reasonable decisions; thus minimizing casualties and property damages. Digital twin enables making predictions and responding fast and accurately, which can create a safer living environment. Going forward, K-water will actively embrace new and innovative technologies to build water management systems that can keep citizens safe.

