

With all corners of the world enduring hardships from global climate change, countries are moving urgently to adopt environmental policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The goal set under the 2015 Paris Agreement is to limit the average temperature increase to 1.5℃ above pre-industrial levels in setting the ceiling target to ensure the survival of human race, while the European Commission is working hard to achieve carbon neutrality with the goal of reducing EU’s average carbon emissions to at least 55% below 1990 levels by 2030. Carbon neutrality warrants steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions at business sites and use new renewable energy in order to reach net zero. With this in mind, K-water is moving proactively to contribute to Korea’s reaching carbon neutrality. Recently, the amount of greenhouse emissions reduced through renewable energy utilization at K-water’s facility sites has far exceeded that of emissions generated, considerably exceeding the goal of net zero. Moreover, K-water is actively replacing 100% of electricity with renewable energy, including solar and hydro energy, by 2050. Water supply is also closely related to carbon neutrality because the electricity used in the process of operating water supply facilities generates greenhouse gas emissions. Here is how K-water is taking measures to achieve carbon neutrality in the process of producing tap water.
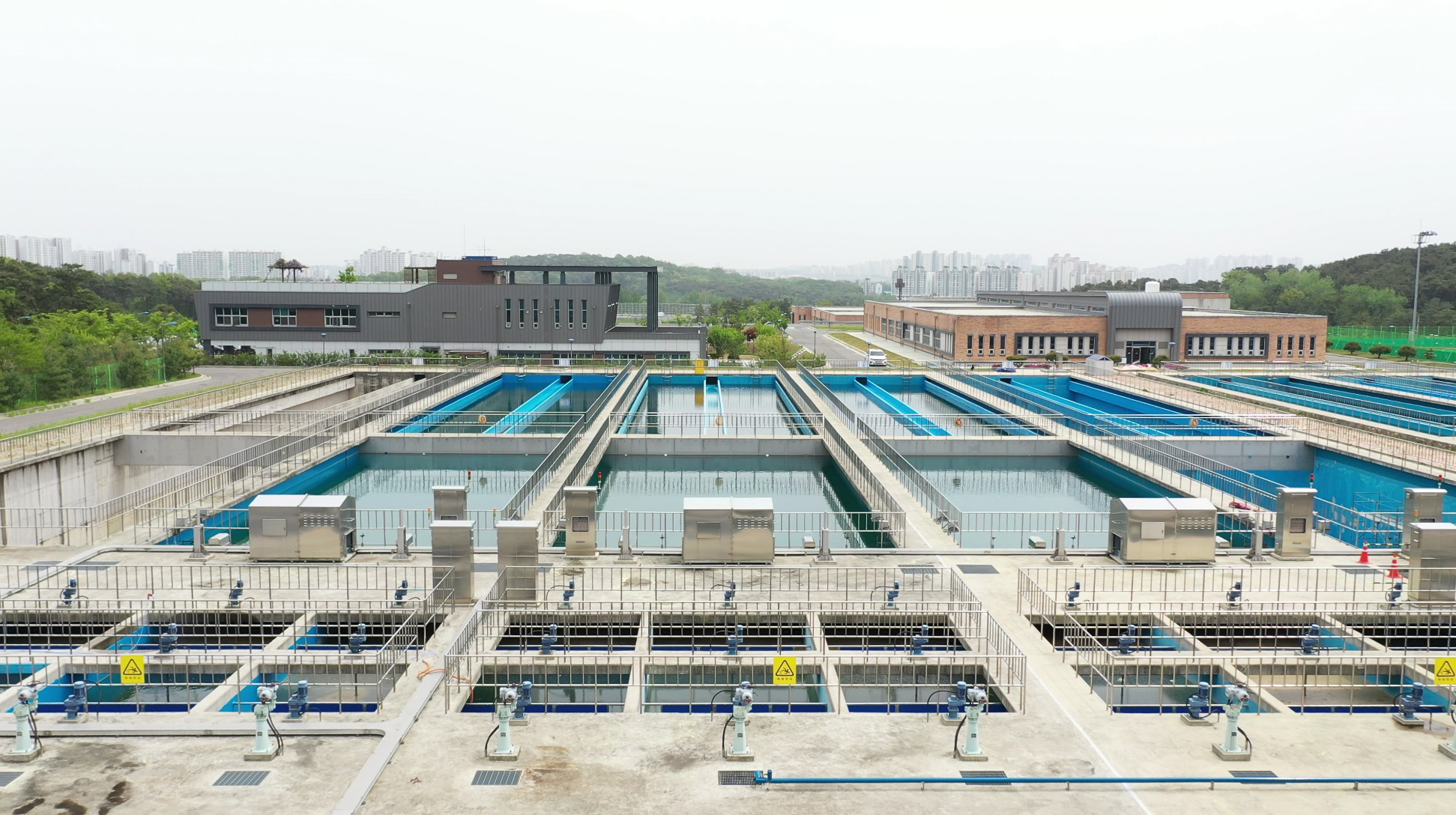
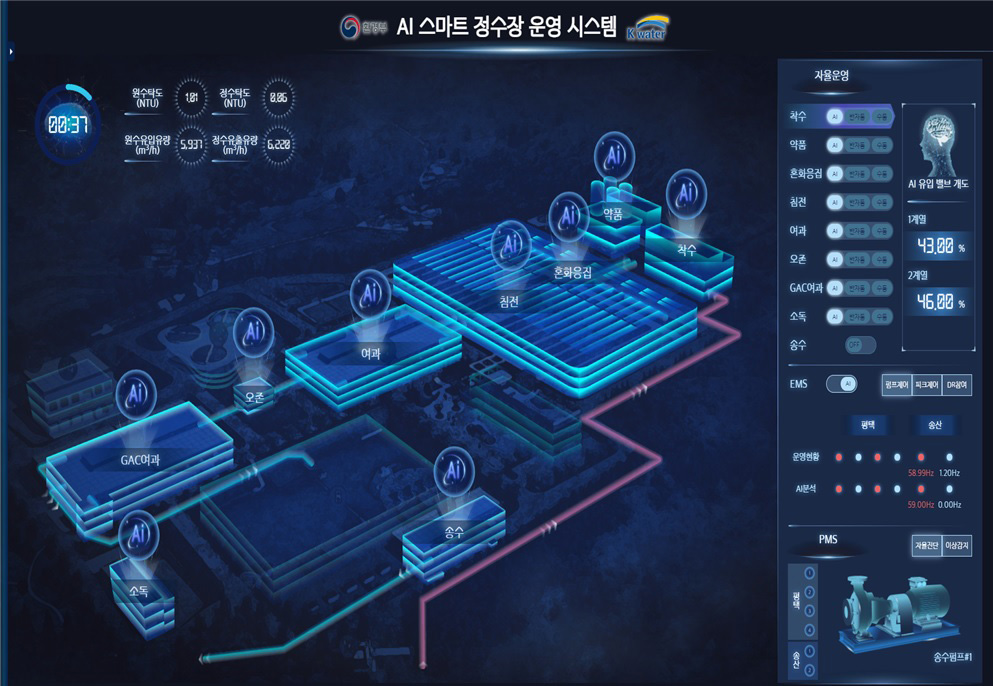

What’s noteworthy is how K-water uses advanced technology to produce low-carbon tap water and make carbon neutrality possible. K-water and the Ministry of Environment have devised the ‘Roadmap of Four Major Strategies for 2050 Carbon Neutrality’ to create and implement a new paradigm for carbon neutrality and energy management. Under this, K-water is to pursue low-carbon tap water production to reduce carbon emissions throughout the entire process of operating water management facilities, and it has been taking measures to minimize carbon emissions generated in the process of tap water production, which includes the 2030 Carbon Emission Reduction Plan for Metropolitan Water Supply Facilities. With the adoption of the energy management system (EMS) and high-efficiency equipment in the entire process of metropolitan tap water production and supply, K-water is optimizing energy use and contributing to carbon emission reduction. EMS is a system designed to analyze and control power use on a real-time basis by applying big data-driven AI algorithms. The data accumulated in real time is analyzed using AI to determine and control the optimal operation of pumps at individual facilities to maintain energy use at optimal levels. In turn, this leads to lower power consumption and lower carbon emissions. In fact, the Hwaseong Water Purification Plant rolled out and pilot-operated an EMS-based smart water purification system in 2021. Given that the pilot operation proved the system to be effective, the smart water purification system will be rolled out at all 43 metropolitan water purification plants. After total rollout of the smart water purification system, K-water will actively pursue carbon neutrality by adopting the cutting-edge AI-enabled technologies to save energy and upgrading old pumps for better performance, with diverse efforts to be undertaken.
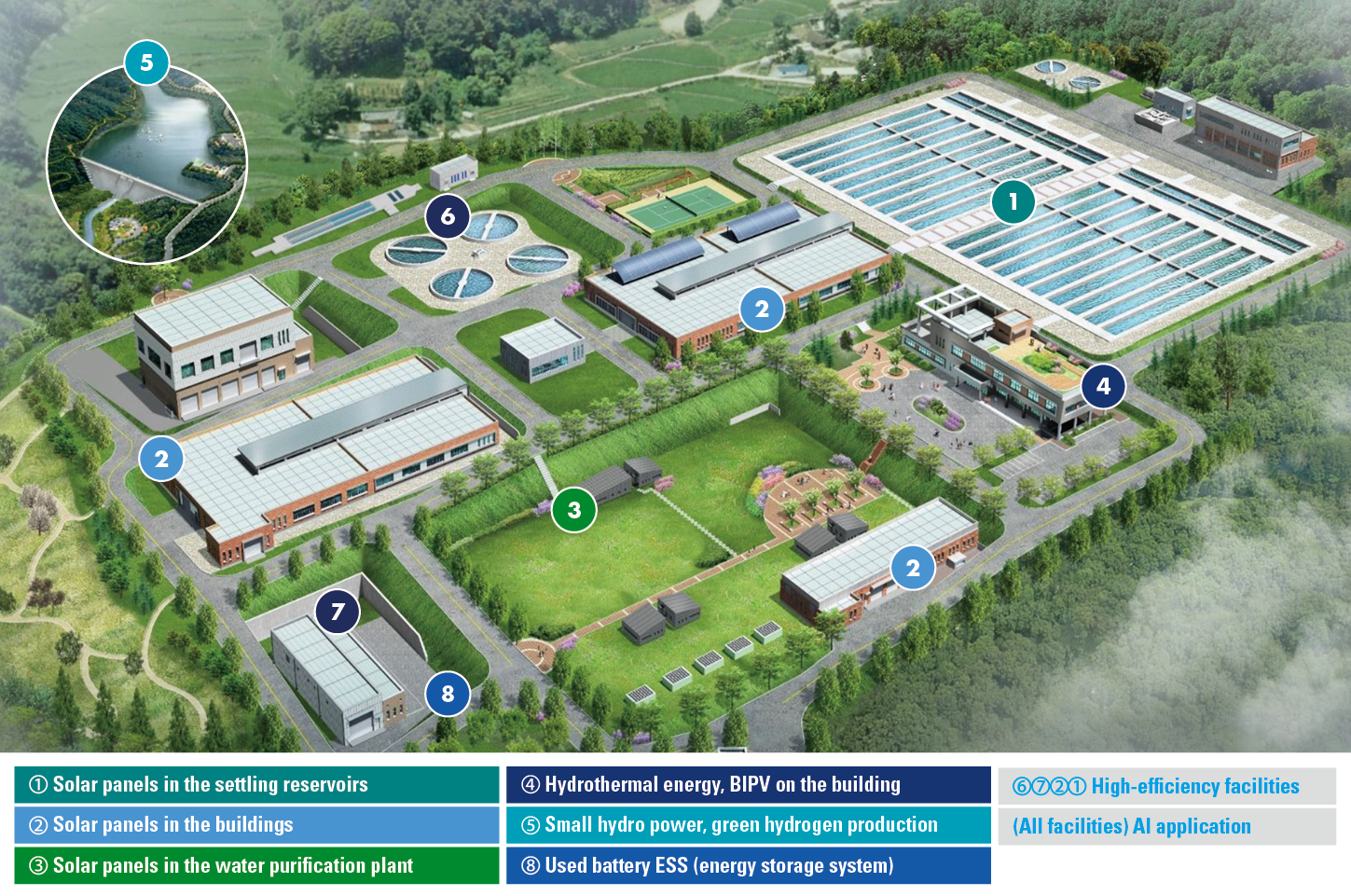

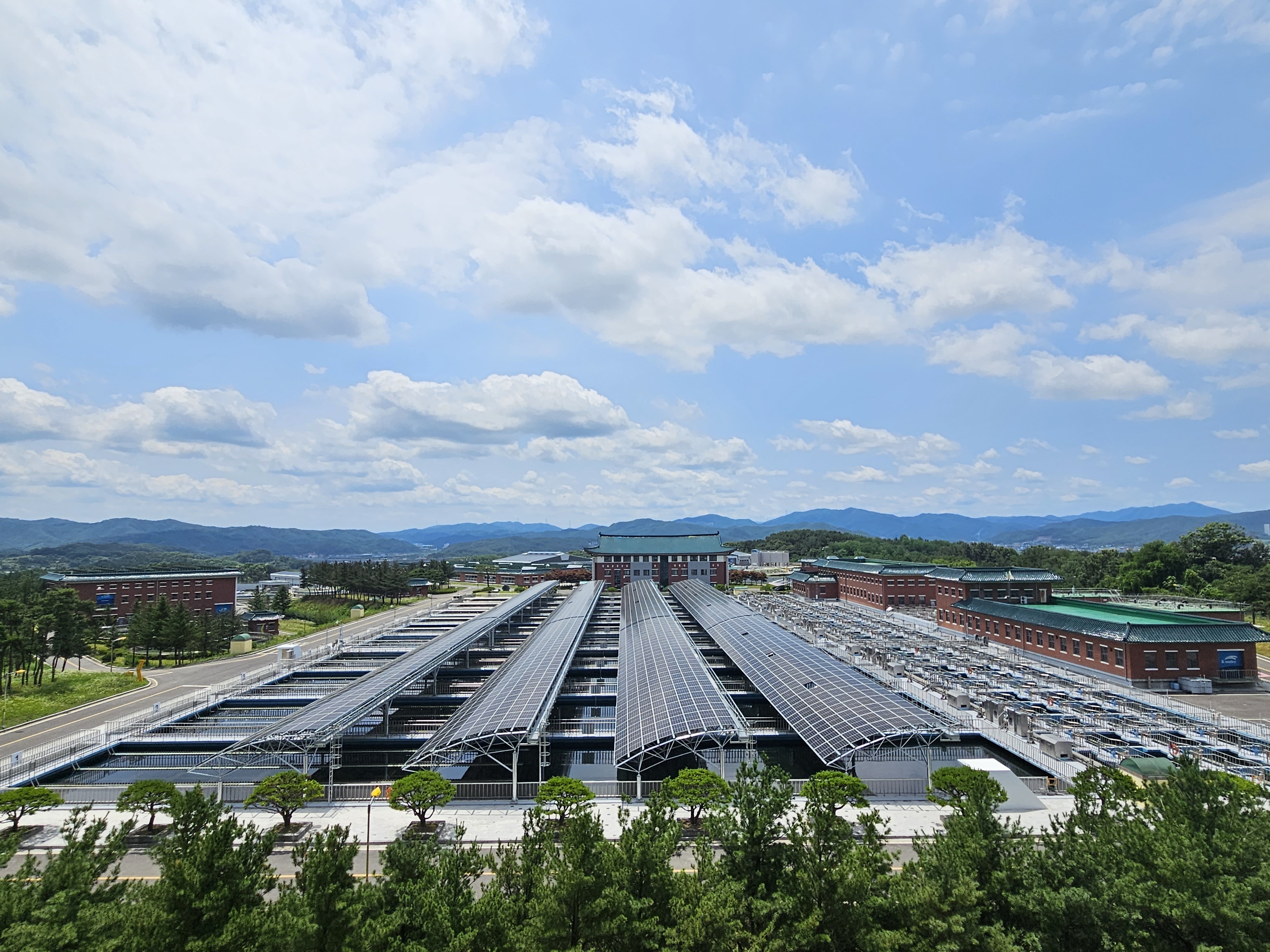
K-water and the Ministry of Environment are working together to create carbon-neutral water purification plants by setting up renewable energy-based power generation facilities on areas of idle land within the metropolitan water purification plants. Currently, five of the 43 metropolitan water purification plants are converted to carbon-neutral water purification plants. K-water plans to install hydro-thermal cooling and heating facilities at metropolitan water purification plants by the end of the year and photovoltaic power generation facilities by 2030 to achieve carbon neutrality by using renewable energy. In addition, research is under way to produce green hydrogen using electricity generated by small hydro power plants at the water purification plants. Green hydrogen, which is forecast to represent 18% of all the global energy sources by 2050, is one of the key elements for carbon neutrality. Since green hydrogen can also be used in other areas, such as electric bus charging stations, besides water purification plants, it will emerge as an effective tool not only to reduce carbon emissions but also to develop new markets for the growth and expansion of Korea’s water industry. Currently, K-water’s Seongnam Water Purification Plant is conducting a green hydrogen demonstration project. K-water plans to expand the green hydrogen production facilities at four water purification plants by 2030.
Green hydrogen is hydrogen generated through electrolysis of water using electricity produced by renewable energy. Green hydrogen is environment-friendly energy with no carbon dioxide emissions involved in its production process.