
-
- Celebrating its 40th anniversary, Chungju Dam takes a new leap forward
-
Having laid the foundation for Korea’s industrialization and urbanization, Chungju Dam is marking the 40th anniversary of its completion by initiating a full-scale transition to future-oriented infrastructure for climate response, AI transformation, and regional coexistence.
K-water held a commemorative event on November 18 at the lawn plaza of Chungju Dam Water Culture Center to celebrate the 40th anniversary of the dam’s completion. The event was attended by members of the National Assembly, Governor of Chungcheongbuk-do, Mayor of Chungju, Mayor of Jecheon, Governor of Danyang County, and around 700 local residents, adding significance to the occasion. Participants looked back on the achievements made by Chungju Dam over the past 40 years and shared future directions centered on climate response and regional cooperation. The event signaled that Chungju Dam is moving beyond being a simple water supply facility and evolving into smart infrastructure that preemptively responds to climate change and grows together with the region.
-
- From a symbol of industrialization to climate response infrastructure
-
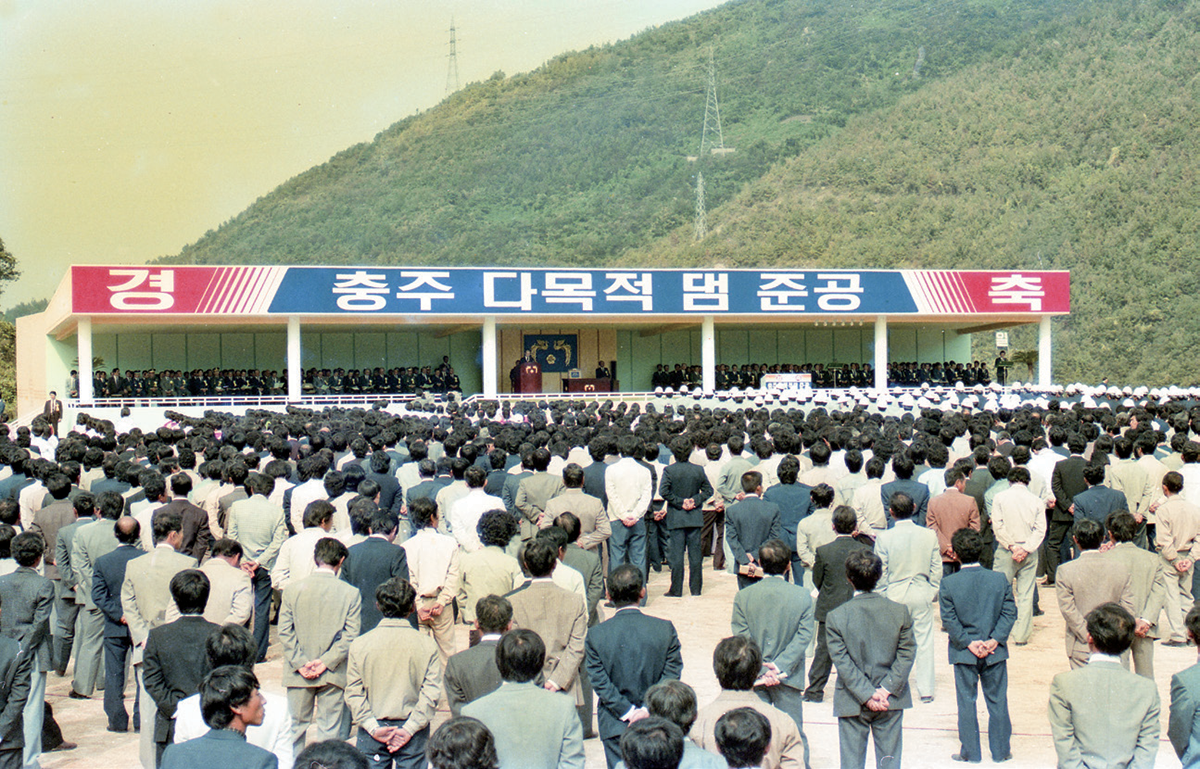
Completed in 1985, Chungju Dam was built to develop water resources in the Namhangang River basin and to supply agricultural, domestic, and industrial water to downstream areas as well as for flood control and hydropower generation. The annual precipitation in the mid and upper regions of Hangang River at that time was around 1,200–1,300 mm with about 60% concentrated in the summer months; thus raising serious concerns about recurring flood damage. In addition, as national economic development plans accelerated in the late 1970s, demand for domestic and industrial water and electricity increased rapidly. To address such imbalance of water resources and challenges in power supply, Chungju Dam was constructed with height of 97.5 m, length of 447 m, and total storage capacity of 2.75 billion m³.
Chungju Dam is the largest multipurpose dam in Korea in terms of basin area (6,648 km²). With its flood control capacity of 620 million tons, it has protected the living areas of 25 million people in the Hangang River basin from major floods, including Typhoon Rusa in 2002 and Typhoon Maemi in 2003. It also supplies 3.38 billion m³ of domestic and industrial water annually, supporting the growth of major inland industrial complexes such as Chungju, Cheongju, Ochang, and Banwol. Moreover, the dam makes substantial contributions to hydropower generation by producing 850 million kWh of clean hydropower annually—enough to cover the electricity demand of approximately 270,000 households. This accounts for about 40% of the total hydropower generation managed by K-water and up to about 25% of Korea’s conventional hydropower. Through these multipurpose functions, Chungju Dam has served as a cornerstone of national economic growth since its completion by providing stable energy essential for Korea’s industrialization and urbanization.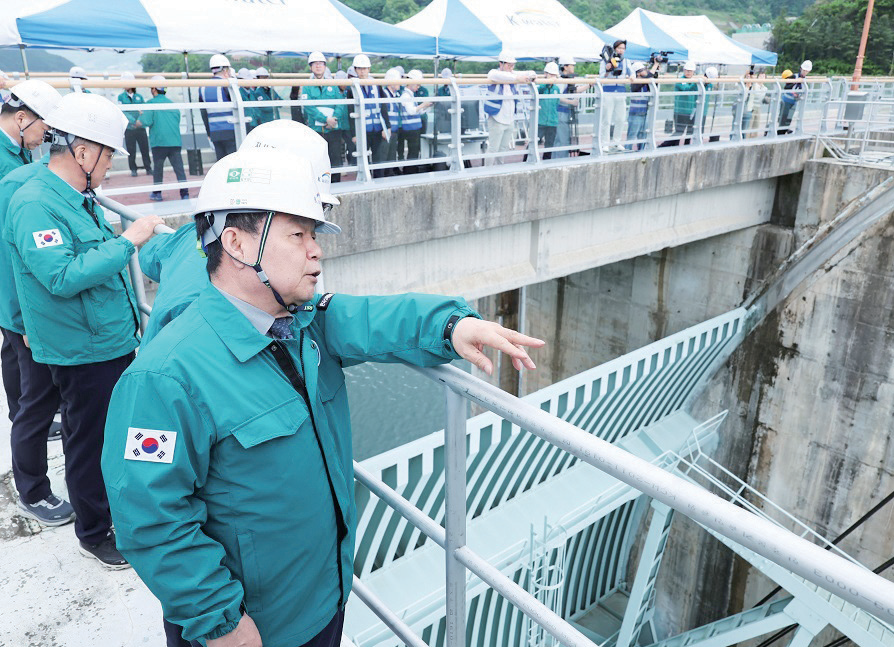
Company-wide flood-season joint training conducted at Chungju Dam Chungju Dam’s 40th-Anniversary Ceremony
-
- Chungju Dam: growing together with the region
-
Building on its achievements over the past 40 years, Chungju Dam is expanding its role to a future-oriented dam for regional coexistence, climate response, and AI transformation. In particular, one of K-water’s key objectives is linking the value of the abundant water stored in Chungju Dam to regional competitiveness through connections with the local economy, culture, and tourism.
The Chungju Lake and Tangeum Lake created with the construction of Chungju Dam are referred to as the “inland sea,” having become representative tourist attractions known for their beautiful natural scenery. Various visitor facilities such as waterfront trails, bicycle paths, and observatories have been established around these lakes, and the area is being utilized as a key hub for promoting local tourism through connections with the Chungju Lake sightseeing cruise, Woraksan National Park, and Cheongpung Lake Cherry Blossom Festival.
With its deep water and calm surface, Tangeum Lake has developed into a notable site for water sports such as rowing and canoeing. Tangeum Lake has become the center of Korea’s rowing venues with its 2,000-meter course, serving as the training site for K-water’s corporate rowing team and as the stage for the Tangeum Lake Rowing Regatta. In addition, K-water has been actively involved in promoting various regional cooperation projects aimed at enhancing the value of the dam and its surrounding areas such as the “Chungju Dam Children’s Carbon Forest Project” and the “Chungju Dam Water Light Trail Project.”
Furthermore, the “Dam Area Support Program” implemented since 1990 has been transformed into a community-led model that enables local residents to identify regional growth initiatives directly and address regional issues; thus establishing a sustainable cooperation framework. For example, the eco-friendly landscape complex “Cheongpung Areum-Green” created through direct participation by residents presents new scenery each season. Launched in 2023 as a local government project, “Jangja Wetland Canoe Experience Center” is Korea’s only waterway-type canoe tour program attracting over 1,000 visitors in its first pilot year and growing into one of Chungju’s signature tourism attractions. In addition, K-water continues to implement various support programs for communities surrounding the dam—such as operating public laundromats, providing on-site home organization services, and offering education support initiatives for future generations—thereby putting regional coexistence into practice.
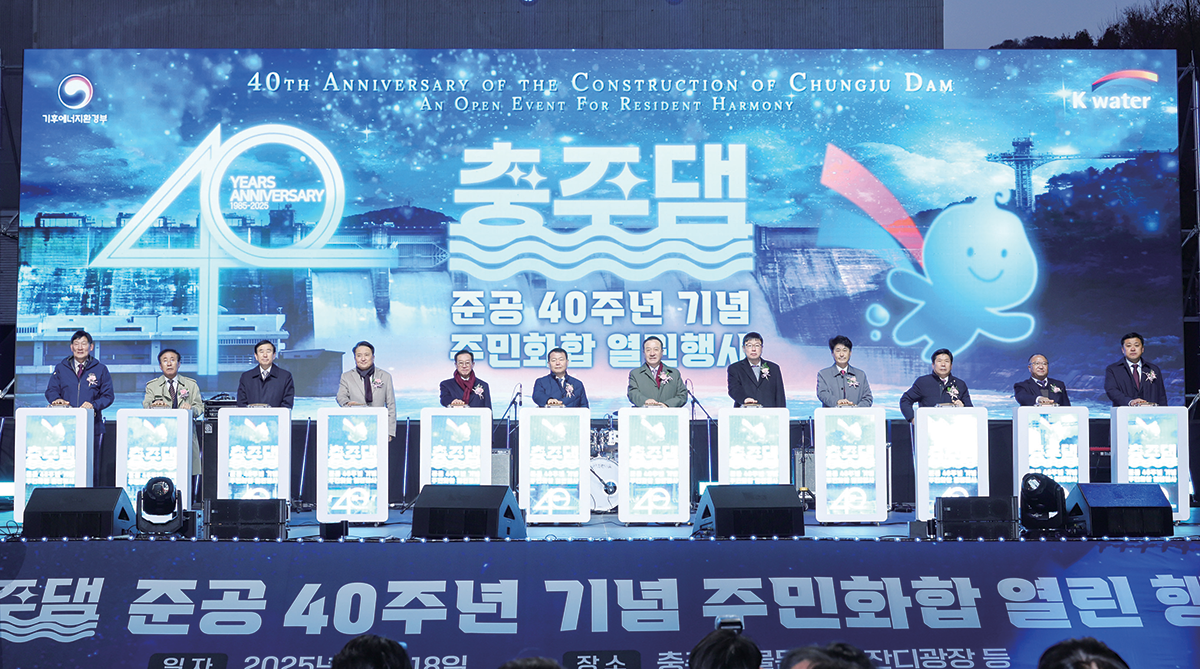

Chungju Dam’s 40th-Anniversary Ceremony -
- A Future-Oriented Dam Leading AI and Energy Transition
-
Responding to the climate crisis and adapting to industrial transformation are emerging as new tasks for Chungju Dam. It is strengthening its water management capabilities by introducing a smart dam operation system based on cutting-edge water management technologies such as digital twins, enabling real-time disaster response and prediction-centered management. Accounting for 52% of flood control in the Namhangang River basin, Chungju Dam secured adequate storage capacity this year by pre-releasing water in preparation for extreme rainfall exceeding 100 mm per hour. Through planned operations utilizing advanced technologies such as digital twins, it secured approximately 1.6 billion ㎥ of flood control capacity, ensuring stable water management without damages in the upstream and downstream regions.
With Korea increasingly recognized as a global AI hub, stable water supply is essential for building advanced industrial infrastructure and producing AI semiconductors. To this end, K-water is integrating super-gap technologies such as digital twins into dam operations and maximizing the productivity and efficiency of water resources through various strategies including Water Positive initiatives. Water secured through these efforts will also be supplied to a semiconductor megacluster being developed in Yongin, envisioned as one of the world’s largest. In addition, Chungju Dam possesses abundant water resources, large-scale power facilities, and wide reservoir surface area, giving it enormous potential for renewable energy development. By leveraging hydro energy and floating solar power, K-water supports the achievement of RE100 and carbon neutrality while also pursuing green hydrogen projects in phases.
Having successfully fulfilled its mission in Korea’s industrialization and urban development, Chungju Dam will move beyond being a national core infrastructure and continue supporting the nation’s energy transformation, advancement into one of the world’s top three AI powerhouses, climate response, hi-tech industrial transition, and balanced regional development. As a future-oriented dam, it will carry these roles forward into the next 40 years.

Panoramic view of Chungju Lake (©Chungju City Hall) 
National Water-Loving Rowing Competition held at Tangeum Lake

 View previous
View previous 이전호 보기
이전호 보기