K-water Report
Entrusted with Water Supply
to Local Communities for 20 Years
“Water Wellbeing for All”
K-water has been entrusted by 23 local governments to operate their water supply facilities since 2004, ensuring that all citizens have access to clean, safe water. This year marks the 20th year of K-water’s entrusted operation of local water supply systems. This edition of K-water Report reviews the major milestones in K-water’s efforts to provide clean and safe drinking water for all.
Text by the Editorial Team Source: Water Supply Planning Department, K-water

Clean Tap Water for Everyone
From drinking coffee in the morning to cooking, cleaning, and taking a shower, water is essential for us to conduct daily activities. In Korea, 97.8% of the population have access to tap water as of 2022. Clean tap water is available almost anywhere in the country. Tap water is supplied to individual households through three major channels in Korea. A metropolitan water supply system supplies raw water or purified water to two or more communities. A local water supply system is operated by a local government to provide water to local residents, and there is a community water supply system. There are 161 water suppliers associated with local governments that supply tap water to local communities. However, water services vary widely in quality due to gaps in budget, water supply conditions, population density, and technology among local governments.
According to the 2022 water supply data, the water rate rationalization rate—referring to water rate as a percentage of tap water production cost—was 82.3% on average for metropolitan cities and 41.4% for counties. According to the benefit principle, water services are provided using revenues from the water bills paid by the people. There is a significant gap between the high cost of water supply and the low water rates. As a result, water suppliers are struggling with chronic deficits, which in turn lead to varying quality of water services including water quality control, water supply service ratio, revenue water ratio, and customer services. Small local governments often experience financial difficulty and find it hard to make any investment in their water supply facilities, creating a vicious cycle.

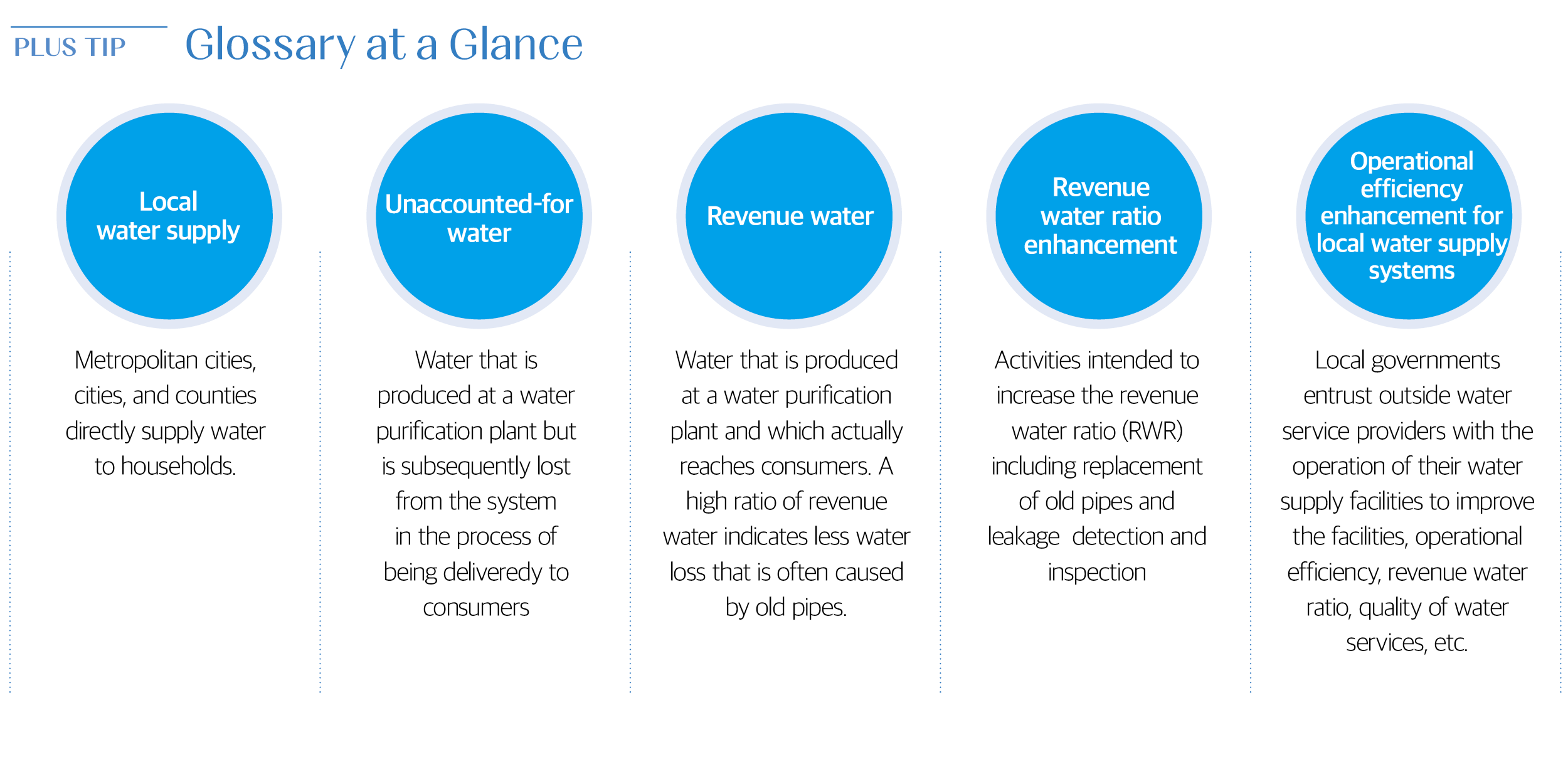
Advanced Technology and New Operational Approach: the Key to Qualitative Growth in Local Water Supply
The Water Supply and Waterworks Installation Act was amended in 2001 to allow local governments to entrust water supply to outside water service providers in an effort to address the financial difficulty facing local governments and narrow the gap in water service quality among different regions. In recognition of its expertise in metropolitan water services and facility operation, K-water was entrusted by the city of Nonsan to operate its water supply system, launching the Operational Efficiency Enhancement Project for Local Water Supply Systems in 2004. Nonsan is the first local government to entrust K-water with water services.
In 2003, the revenue water rate of Nonsan was 58%. K-water acted promptly and replaced outdated pipes that might cause leaks and negatively affect water quality. Moreover, K-water automated the manually operated facilities and put in place a remote-control operation system. Consequently, RWR increased to 80% and customer satisfaction improved as customer complaints were handled immediately. The project began to spread across the country; currently, K-water is operating local water supply systems for 23 local governments nationwide.

K-water raises the water service quality and public confidence in tap water to a new level
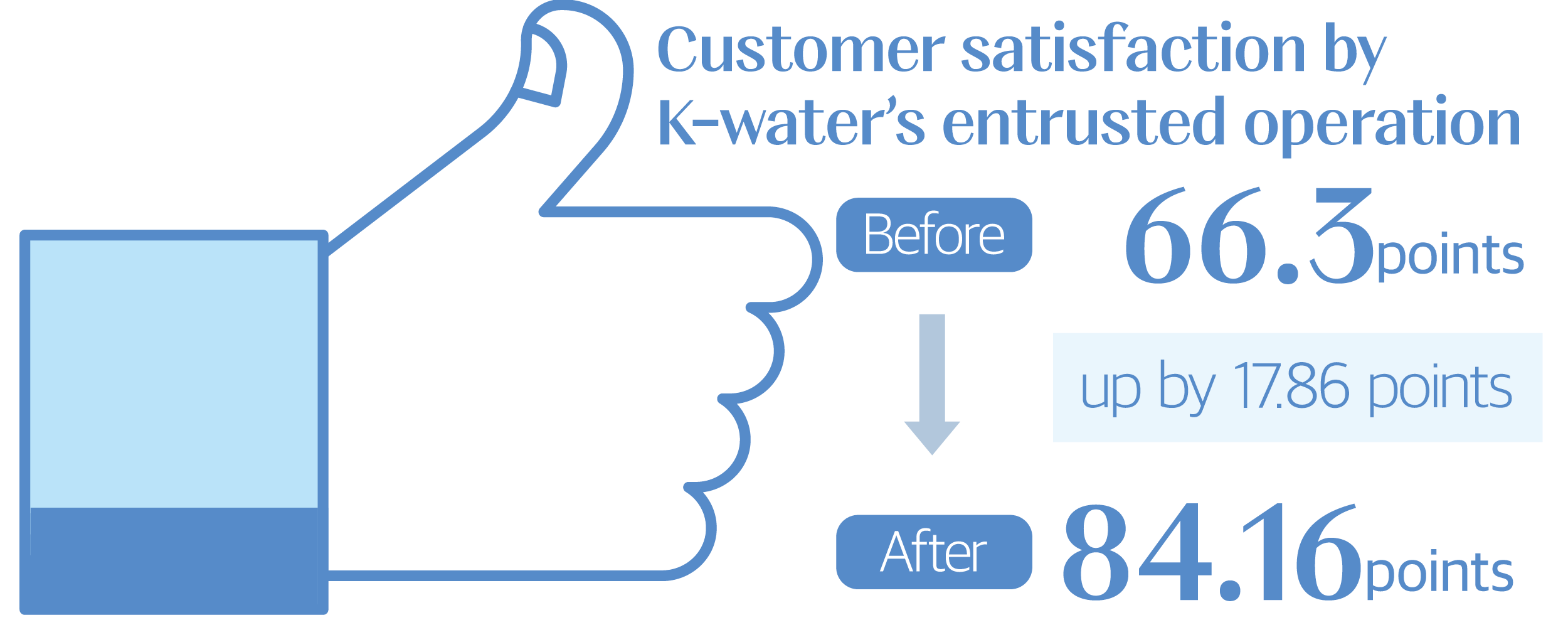
K-water has improved the operational efficiency of local water supply systems by replacing outdated pipes and pumps and actively incorporating digital technology into water management. The average RWR of 23 local governments prior to K-water’s entrusted operation, which stood at 60.1%, rose to 85.1% after K-water took over the operation of their water supply systems. The higher RWR translated into approximately 1.49 billion tons in water savings from leaks in 2023, resulting in a virtuous cycle of cost reduction and a higher water supply service ratio. Furthermore, K-water is offering a wide range of water-related services to boost local residents’ trust in tap water and provide easy access to water information. All these efforts proved to have made a significant difference in the lives of local residents. The 2023 Local Water Service Customer Satisfaction Survey found that customer satisfaction rose 18 points from a year ago to reach an all-time high of 84.16 points. Going forward, K-water will continue to work closely with local communities and provide top-tier water services.

